
With the shift to distributed workforces and digital business models, cloud infrastructure and tools have become indispensable to the modern enterprise. But this growing reliance on the cloud also comes with a corresponding increase in security risks and breaches.
The question is: When it comes to protecting public, hybrid, or multi-cloud environments, who should take ownership, the organization in question or the cloud service provider (CSP)?
The answer isn’t always definite, which is why cloud security frameworks often follow the shared responsibility model—an approach that delineates accountability and responsibility for all parties involved. Read on to learn more about what this entails.
Cloud security is a shared responsibility
In the past 18 months alone, 98% of organizations experienced at least one data breach in the cloud, according to a 2021 report. While an integral aspect of the IT landscape, cloud environments present a broader attack surface through remote endpoints, unsecure devices, and unmanaged data access from across the globe. Failure to secure these will lead to costly data breaches that can impact everything from reputation to bottom line.
Organizations that employ the services or IT infrastructure of a third-party cloud vendor might mistakenly assume that cybersecurity initiatives are the responsibility of the provider alone. However, protecting data, applications, and assets hosted in the cloud needs to be a shared effort.
While it may vary from case to case, it is important to identify which areas the vendor should take ownership of, which ones are in the hands of the organization, and which ones are the responsibility of both parties. Clearly defining this scope of responsibilities will help create a well-rounded cloud security strategy that covers all vulnerabilities and risks.
To start off, it helps to think of cloud security as consisting of: (1) security of the cloud and (2) security in the cloud.
1. Security of the cloud
The cloud environment itself is the responsibility of the CSP. In most cases, the provider is accountable for securing the global infrastructure in which the platform is built upon, the host operating system, and even the physical security of the cloud service, among others. Their security efforts include a wide array of activities such as threat monitoring, preventing unauthorized access, and disaster and incident response.
For example, a high-profile cybersecurity attack in 2020 involved malware infection “of the cloud”—in this case, the cloud infrastructure servers hosted in the Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud. Several Windows and Linux machines inside an AWS data center were compromised through a sophisticated rootkit that allowed attackers to remotely control servers and funnel sensitive corporate data.
In an investigation of the breach, Sophos pointed out that the method employed could bypass most firewalls, even the robust, boundary firewall for EC2 instances provided by AWS SGs in this case. However, they highlight that “this firewall does not eliminate the need for network administrators to keep all external-facing services fully patched.” They also point out that the default installation for the SSH server requires extra steps for extra protection against attacks.
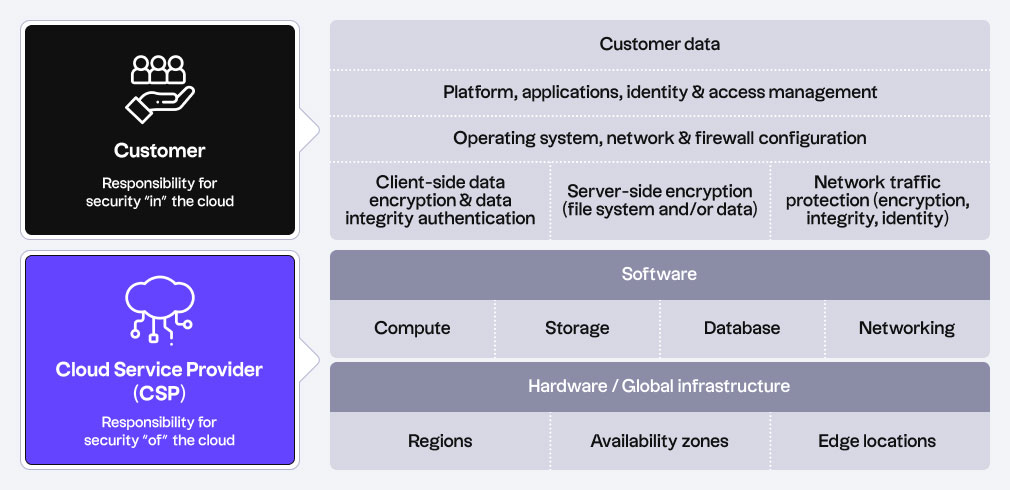
2. Security in the cloud
Ensuring security within the cloud environment, however, is the responsibility of the user’s cybersecurity team. This includes managing and controlling the applications, data, and other assets hosted within the cloud service. Organizations are usually accountable for implementing proper access controls, ensuring data encryption and integrity, configuring network security and firewalls, and even ensuring compliance to regulatory standards.
This is something that should be top of mind for any organization leveraging cloud platforms, since up to 95% of breaches in the cloud are caused by human errors—mistakes that could easily be avoided with proper security controls around access credentials, data sharing, and third-party access, among others.
For example, over 100 pitch decks and source codes from 10 to 15 companies were recently compromised because of a misconfiguration of cloud security buckets. This failure to properly secure data assets resulted in highly sensitive internal data being compromised. While experts are unsure who was accountable in this case, the vpnMentor research team points out that “the shared security model puts the burden of properly securing data assets in the hands of the user.”
Doing one’s part in data protection
Without the proper security policies and controls in place, organizations can face costly data breaches and cyber attacks that can impact everything from reputation to the bottom line. To ensure security in the cloud, organizations need to define and understand where the provider’s responsibility begins and where it ends. But while the parameters of the shared security model may vary depending on the provider or business model being followed, one thing is for certain: organizations and users must keep cloud security top of mind.





